Salesforce Commerce Cloud offers a sales tax calculation feature within the platform. Salesforce Commerce Cloud Storefront can also be integrated with various third-party tax calculation systems to help businesses accurately determine the applicable tax rates.
Once the tax is calculated behind the scenes based on the shipping address entered by the customer, the tax amount will be displayed on the storefront, like below (screenshot from SFRA). In this blog post, let’s see how to use SFCC tax tables to calculate the taxes for products.
What is a taxation policy?
A taxation policy is a set of rules and regulations that determine how taxes are calculated and displayed on a website or in an organisation.
There are two different taxation policies.
- Net: The net taxation policy does not include tax in the product’s selling price.
- Gross: The Gross Taxation Policy consists of the tax on the product’s selling price.
One needs to select the taxation policy at the time of site creation. Changing the taxation policy once the site is created is only possible with help from the support team.
What is a tax table, and how do you configure tax tables?
A tax table is a chart or list that showcases the various income levels and products, individual tax rates, and amounts.
- To calculate taxes for various jurisdictions, tax tables are used.
- It can be used to figure out the tax rate for a particular location or area, like a state or province, as well as to calculate taxes for various goods and services.
- In merchant price books for B2C commerce, tax tables can be configured.
- It can be used to determine whether the prices for goods and services are treated as net prices or gross prices based on the taxation policy.
Tax tables are tax rate mappings with the tax classes and tax jurisdictions. To configure tax tables in Salesforce Commerce Cloud, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to Merchant Tools > Ordering > Taxation to start with the tax table configuration tab.
2. Under the General Tab, you can choose Map Address To with Jurisdiction Mapping, Jurisdiction Mapping, or Jurisdiction ID. Using jurisdiction mapping, we can choose two shipping address fields (Address Mapping 1 and Address Mapping 2). Using Jurisdiction ID, you can select only one address field (Only Address Mapping 1). Address Mapping 2 is not applicable for the Jurisdiction ID option.
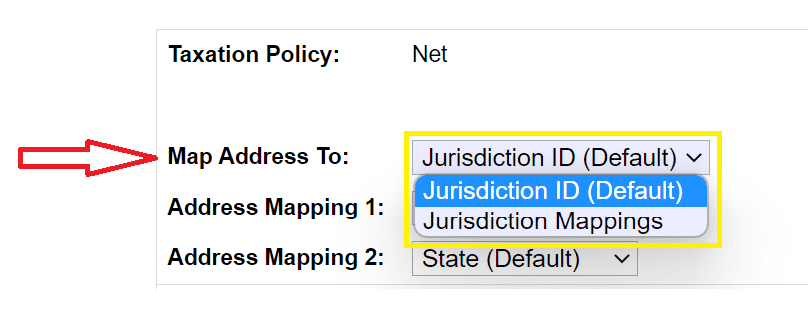

3. Jurisdiction ID vs Jurisdiction Mappings
| Jurisdiction ID | Jurisdiction Mappings |
|---|---|
| A jurisdiction ID is a unique identifier for a tax jurisdiction, a geographic area with a specific set of tax laws and regulations. | A jurisdiction mapping links a specific tax jurisdiction to a particular customer shipping address. |
A tax class is a collection of tax rates for different tax jurisdictions. Under the Tax Class Tab, we can create or delete tax classes for a site. We can make a tax class default for a site. The default tax class is used for products and services that aren’t assigned to a particular tax class. We can create a new tax class and delete the existing tax classes.
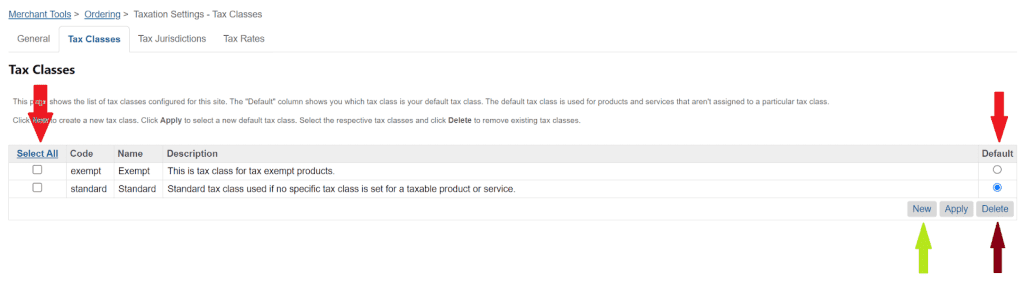
5. Tax classes should be created and assigned for products and shipping methods.
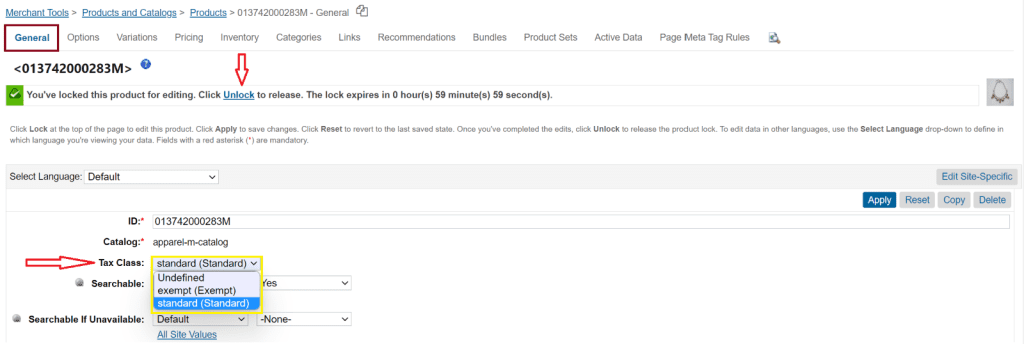
6. To assign tax classes to products, navigate to Merchant Tools > Products and Catalogues > Products, select a product, and you will be landed on a product configuration page as shown below. Click on lock, as products are by default locked for modification of data.
7. Select the applicable tax class from the Tax Class drop-down.
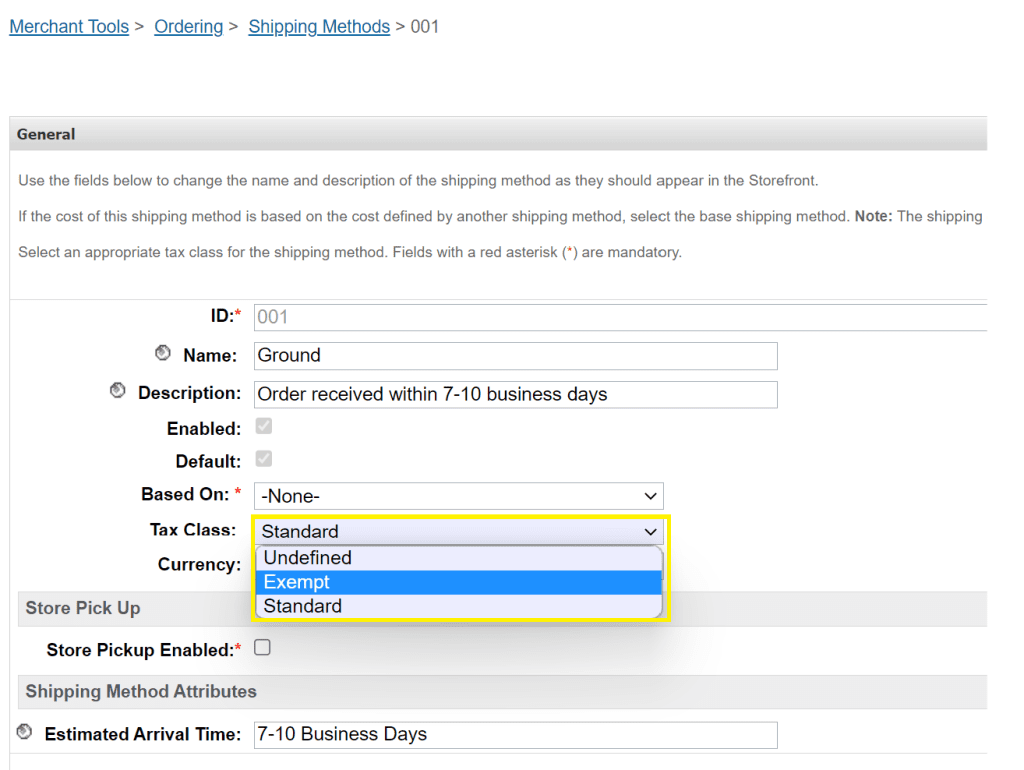
8. To assign tax classes to shipping methods, navigate to Merchant Tools > Ordering > Shipping Methods and select the shipping method you want to configure. You will be landed on a Shipping Method Configuration page, as shown below. Select the applicable tax class from the Tax Class drop-down.
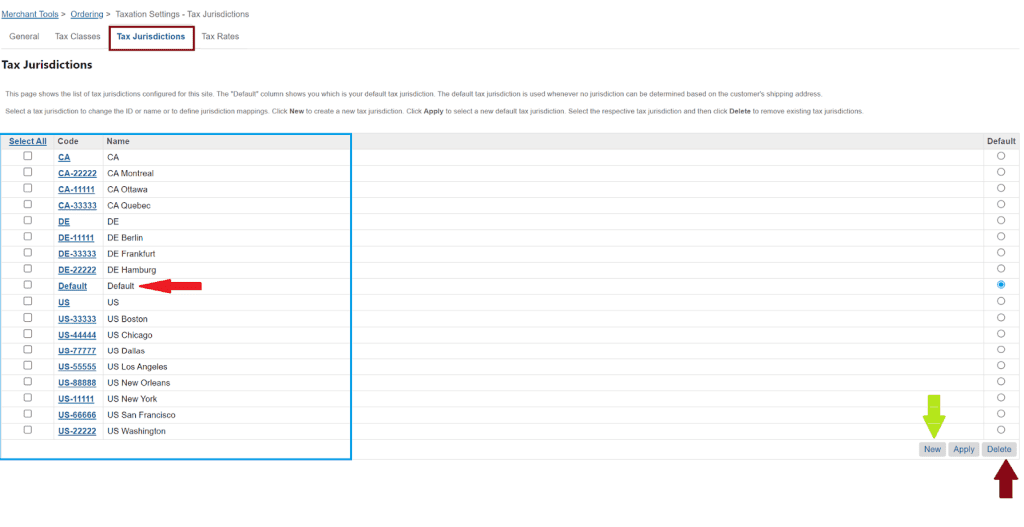
9. A tax jurisdiction is a rule based on the customer’s shipping location to calculate the tax rates. Under the Tax Jurisdictions Tab, we can find a list of tax jurisdictions configured for a site. We can set tax jurisdictions as the default for a site. The default tax jurisdiction is used whenever no jurisdiction can be determined based on the customer’s shipping address. We can edit the mapping, delete it, and create new jurisdictions under this tab.
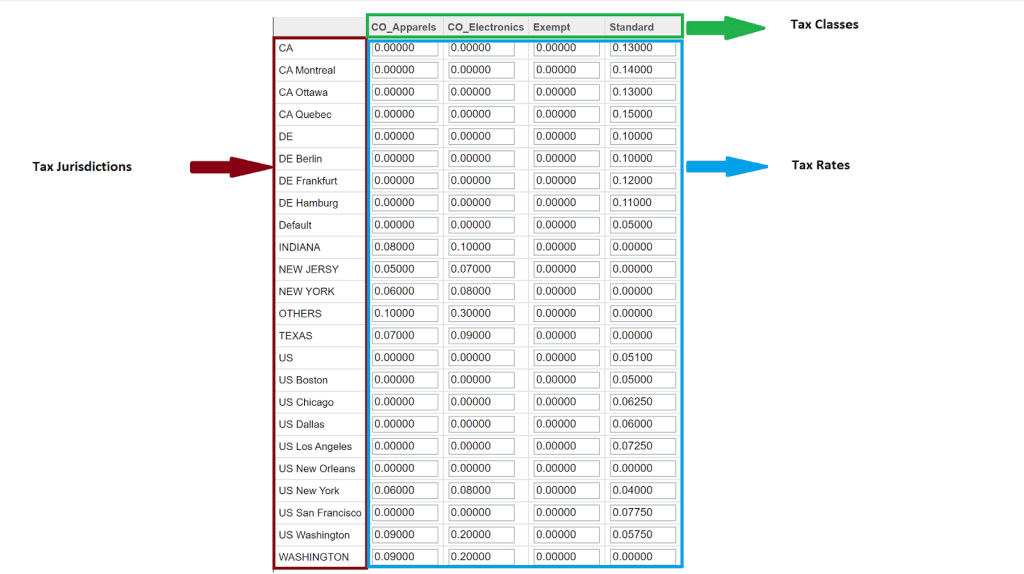
Under the Tax Rates tab, we can configure the tax rates for each tax jurisdiction. Please see the below image for reference.
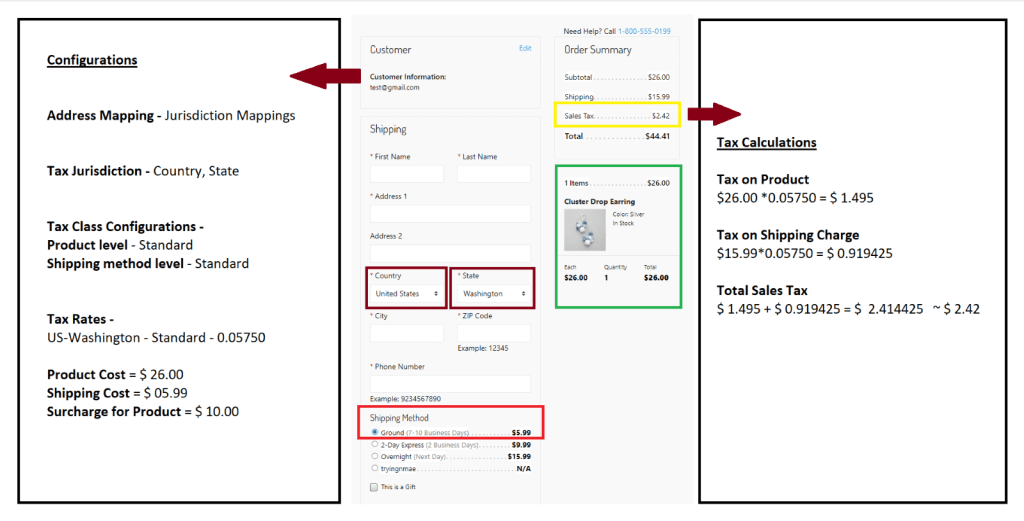
Tax rate lookup use cases
- Calculations of tax rates include tax jurisdictions, tax classes, and tax rate configurations.
- On the checkout page, the selection of country, state, or postal code points to a jurisdiction created for shoppers’ selected shipping location.
Note: Address mappings are relative to the jurisdiction ids and jurisdiction mappings.
- Tax classes are mapped at the product and shipping method levels to define a tax rate under the tax rates tab.
- Here are examples of how a lookup happens as per the tax table configurations in the images below.
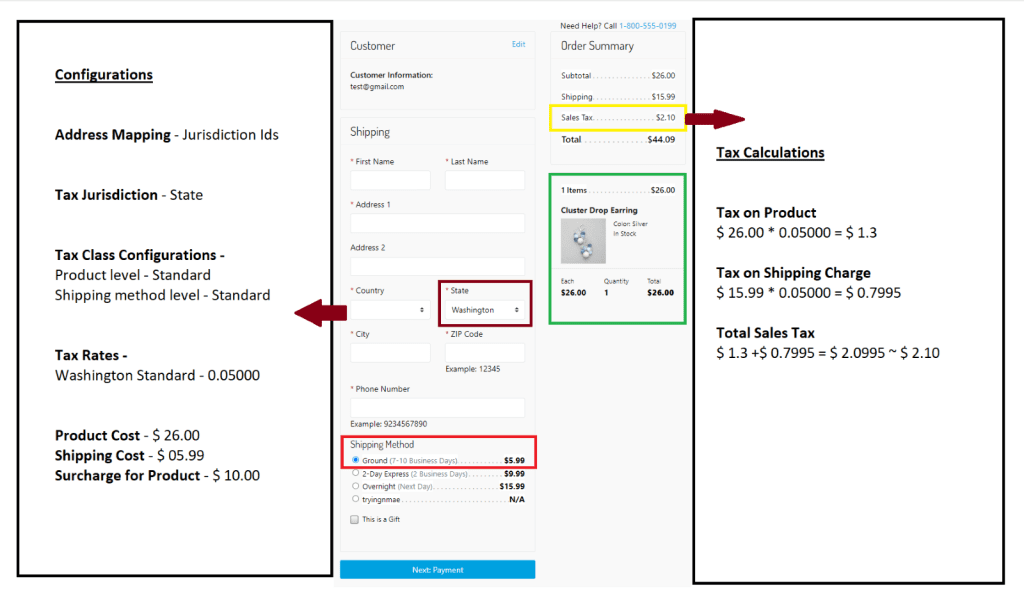
Merchants can set tax rules in Salesforce Commerce Cloud to control how taxes are calculated and applied to orders submitted to their online store. The Commerce Cloud platform itself is used to set up and maintain these tax tables. Avalara, Vertex, TaxJar, and other third-party tax calculation systems also offer a solution that can be integrated with Commerce Cloud to help merchants calculate and apply taxes to orders, and Salesforce Commerce Cloud Tax tables can be used in parallel as a backup for 3rd party tax calculation systems.
Quick summary
- Salesforce Commerce Cloud offers a sales tax calculation feature within the platform.
- The storefront can be integrated with various third-party tax calculation systems to accurately determine the applicable tax rates.
- Taxation policies can be net or gross.
- Tax tables can be configured to determine tax rates for specific locations and products.
- Tax classes and tax jurisdictions need to be assigned to products and shipping methods.
- Tax rates can be configured for each jurisdiction.
- Salesforce Commerce Cloud can be used alongside third-party tax calculation systems as a backup.
Click here to read The Power of Embedded Commerce: Revolutionising E-commerce with Salesforce Commerce Cloud.